Lycopene ameliorates systemic inflammation-induced synaptic dysfunction via improving insulin resistance and mitochondrial dysfunction in the liver–brain axis†
Abstract
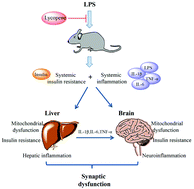
Systemic inflammation is an important determinant of synaptic dysfunction, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. Lycopene (LYC), a major carotenoid present in tomato, is regarded as a nutraceutical that has significant antioxidant and anti-obesity bioactivities. In the current study, we randomly divided 3-month-old C57BL/6J mice into 3 groups: the control, LPS and LPS + LYC groups (LYC, 0.03% w/w, mixed with normal chow) for 5 weeks, and then mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (0.25 mg kg−1) for 9 days. Our results demonstrated that LYC supplementation effectively attenuated LPS-elicited neuronal damage and synaptic dysfunction through increasing the expressions of neurotrophic factors and the synaptic proteins SNAP-25 and PSD-95. LYC ameliorated LPS-induced insulin resistance and mitochondrial dysfunction in the mouse brain and liver. LYC alleviated the neuroinflammation and hepatic inflammation. Furthermore, LYC decreased the circulating levels of insulin and proinflammatory mediators LPS, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. In conclusion, these results indicated that the supplementation of LYC might be a nutritional preventive strategy in systemic inflammation-induced synaptic dysfunction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...