Simulated gastrointestinal digestion of inclusion complexes based on ovalbumin nanoparticles and conjugated linoleic acid
Abstract
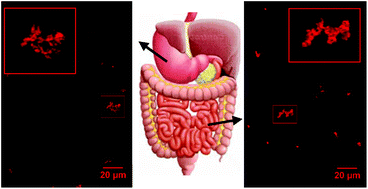
The objective of this work was to obtain and characterize conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) delivery systems based on ovalbumin nanoparticles (OVAn1 and OVAn2) and to study their behaviour under a standardised static in vitro digestion model. OVAn1 and OVAn2 were obtained by heat treatment (85 °C, 5 min, pH 11.35 and 7.5, respectively). OVAn1 and OVAn2 had hydrodynamic diameters of 24.63 ± 0.04 and 92.0 ± 0.2 nm, respectively, showing no significant differences in ζ potential values (p < 0.05) at pH 7.0. CLA nanocomplexes were examined in terms of size and ζ potential at pH 3.0 and 7.0, highlighting that binding of CLA caused an increase in size for OVA and both OVA nanoparticles. Morphological characterization was performed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CSLM) finding that OVA and OVA nanoparticles had a circular shape. Also, the CLA encapsulation efficiency (EE) for OVA and OVA nanoparticles was studied, yielding EE values greater than 97% for all systems. Finally, systems were assayed for a standardized in vitro gastrointestinal digestion model considering gastric and intestinal steps. Macroscopic appearance, CSLM images and quantification of CLA retention by HPLC were evaluated after digestion. All the systems showed the formation of macroscopic aggregates both in gastric and intestinal phases, which generated a visible precipitate. In all systems, CSLM confirmed the presence of numerous undefined-form aggregates. Finally, high CLA retention (around 99%) was found for native protein and nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...