Comparative oral and intravenous pharmacokinetics of phlorizin in rats having type 2 diabetes and in normal rats based on phase II metabolism†
Abstract
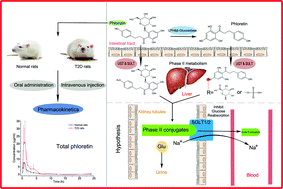
Phlorizin (PHZ), a type of dihydrochalcone widely found in Rosaceae such as apples, is the first compound discovered as a sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitor. It has been confirmed to improve the symptoms of diabetes and diabetic complications effectively. Like other flavonoids, the bioavailability challenge of PHZ is the wide phase I and II metabolism in the digestive tract. In this study, we investigated the pharmacokinetics and contribution of phase II metabolism after the oral and intravenous administrations of PHZ in rats having type 2 diabetes (T2D) and in normal rats. The phase II metabolism characteristics of PHZ were investigated by treating plasma samples with β-glucuronidase/sulfatase. The contribution ratio of phase II metabolism of PHZ ranged from 41.9% to 69.0% after intravenous injection with three doses of PHZ in normal rats. Compared with the observations for normal rats, AUC0−t and Cmax of PHZ significantly increased and T1/2 of PHZ significantly decreased in T2D rats. PHZ was converted into phloretin (PHT) through an enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction, and PHT was further transformed into conjugates with glycose after both oral and intravenous administrations. Moreover, it was found that the bioavailability of PHZ was about 5% in T2D rats, which was significantly higher than that in normal rats (0%). In conclusion, compared with the observations for normal rats, the pharmacokinetic characteristics of PHZ significantly changed in T2D rats through oral and intravenous administrations. The bioavailability of PHZ significantly increased in T2D rats. Besides, the phase II metabolites of PHT were the major existing forms in blood after oral and intravenous administrations. Our results indicated that the phase II metabolism characteristics of PHZ should be considered when PHZ is applied for the treatment of diabetes as a drug or functional food.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...