Effects of dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid supplementation on the intestinal functions in weaning piglets†
Abstract
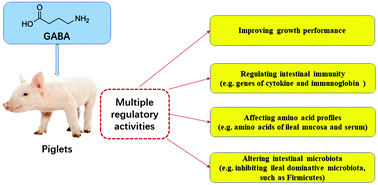
This study aims to investigate the effects of dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) supplementation on the growth performance, intestinal immunity, intestinal GABAergic system, amino acid profiles and gut microflora of the weaned piglets. Totally sixteen healthy piglets were randomly assigned into two groups to be fed with the basal diet (Con group) or the basal diet with GABA (20 mg kg−1) supplementation. Body weights and feed intakes were monitored weekly. Piglets were sacrificed after 3 weeks of GABA supplementation to collect the blood, ileum, ileal mucosa and luminal content. Immune-associated factors, GABAergic system, amino acid profiles, and microbiota in the ileum and serum amino acid profiles were explored. The results showed that GABA supplementation improved the growth performance and modulated the intestinal immunity with inhibiting the gene expressions of IL-22, proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-18), and Muc1, but promoted the expressions of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-10), TLR6 and MyD88. GABA regulated a few components of the intestinal GABAergic system, increased the levels of most amino acids in the ileal mucosa but reduced the serum amino acid profiles. GABA regulated the population and diversity of intestinal microbiota, such as the abundances of the dominant microbial populations, the community richness, and diversity of the ileal microbiota. In conclusion, GABA supplementation modulated the intestinal functions, including intestinal immunity, intestinal amino acid profiles and gut microbiota, and the results can be helpful for understanding the functions of GABA in the intestine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...