Can cerium oxide serve as a phosphodiesterase-mimetic nanozyme?†
Abstract
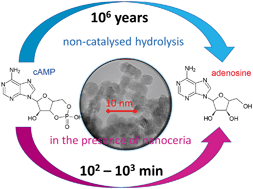
The enzyme-mimicking activities of nanocrystalline cerium oxide (nanoceria) are well recognized, and its ability to accelerate the dephosphorylation of simple organophosphates and energetically rich biomolecules such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) has previously been proven. Here, we hypothesized that cerium oxide may also be effective in the cleavage of more-resistant phosphoester bonds, namely, those in 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), which mimics the 3′–5′ phosphodiester bonds in nucleic acids well. The nanoceria-accelerated dephosphorylation of cAMP proceeds on the time scale of 102–103 min (compared with 106 years in the absence of cerium oxide) and is only slightly affected by pH. The dephosphorylation activity is highly specific to cerium oxide, as it was not observed with oxides of neighbouring lanthanides (La2O3, Pr6O11, and Nd2O3) or with other metal oxides. The nanoceria also decomposed the organophosphate pesticides parathion and paraoxon methyl and the chemical warfare agents soman and VX. A new model was proposed to describe the activation of dephosphorylation reactions in the presence of (nano)ceria. An unusual phosphatase-mimetic activity resulted from an interplay between properly arranged Ce3+ and Ce4+ cations and cerium-activated hydroxyl groups. The special structural motifs responsible for the phosphatase-mimetic activity are dynamically created and regenerated on the surface of cerium oxide thanks to the Ce3+/Ce4+ switching ability of cerium cations and a flexible oxygen-conducting structure of cerium oxide.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...