Dissolution kinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticles: real-time monitoring using a Zn2+-specific fluorescent probe†
Abstract
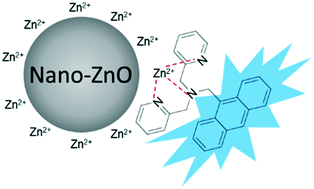
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (nano-ZnO) are emerging pollutants that have raised concerns of potential environmental risk. Previous studies demonstrated that the toxic effects of nano-ZnO towards aquatic organisms were mainly contributed by the dissolved Zn2+. Thus, identifying the dissolution kinetics is important in ecotoxicological research regarding nano-ZnO. Most currently available methodologies (e.g. inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry – ICP-MS analysis) for studying the dissolution of nano-ZnO require the separation of the dissolved Zn2+ from nano-ZnO by ultrafiltration, which are time-consuming and may cause inaccurate results. To overcome these limitations, this study reported a fluorescence method for monitoring the rapid dissolution kinetics of nano-ZnO in aquatic environments. A Zn2+ sensor, namely, (9-anthrylmethyl)bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-amine (AMBPA), was used for the quantification of Zn2+ dissolved from nano-ZnO. AMBPA showed high specificity towards Zn2+ relative to nano-ZnO. Also, the small effect of interfering cations and anions on the fluorescence emission of Zn2+–AMBPA proved the selectivity of AMBPA towards Zn2+. The measurement of Zn2+ dissolved from four types of nano-ZnO by the proposed fluorescence method was compared with that by ICP-MS analysis following ultrafiltration. The proposed fluorescence method showed higher capability in terms of monitoring the rapid dissolution kinetics of nano-ZnO than the ICP-MS method, given that the former could monitor the real-time dissolution kinetics of nano-ZnO. This is important for understanding the dynamic behaviors of nano-ZnO at the early stage of reaction. The proposed fluorescence method described in this study is a suitable tool for studying the dissolution kinetics of nano-ZnO in aquatic environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...