The effects of ZnO nanoparticles on leaf litter decomposition under natural sunlight†
Abstract
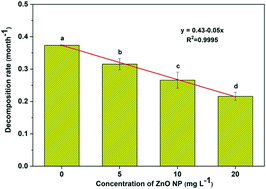
To comprehensively assess the effects of ZnO nanoparticles on freshwater decomposition processes under natural sunlight, we conducted an indoor microcosm experiment on Populus nigra L. leaf decomposition with ZnO nanoparticles (5, 10, and 20 mg L−1) under simulated sunlight. A significant and negative relationship between decomposition rate and ZnO nanoparticle concentrations was observed after 30 days of exposure. ZnO nanoparticles significantly inhibited extracellular enzyme activities, dehydrogenase activities and fungal biomass as well as impacting fungal community structures. Additionally, the exposure to ZnO nanoparticles increased microbial antioxidant activities and 5 mg L−1 of ZnO nanoparticles led to the greatest increase. Importantly, the activities of carbon-related enzymes were significantly inhibited by ZnO nanoparticles, but leaf carbon decomposition was stimulated in the microcosms containing 10 and 20 mg L−1 of ZnO nanoparticles, suggesting the possible contribution of ZnO nanoparticles' physicochemical properties under sunlight to leaf decomposition. The information provided here on the effects of different concentrations of ZnO nanoparticles under sunlight will help us to better evaluate the impacts of ZnO nanoparticles on stream functioning.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...