Radium in hydraulic fracturing wastewater: distribution in suspended solids and implications to its treatment by sulfate co-precipitation†
Abstract
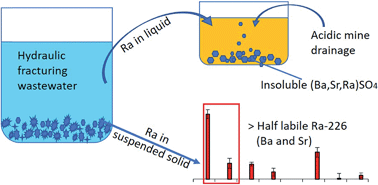
High concentrations of barium (Ba), strontium (Sr) and radium (Ra) are present in both the liquid and suspended solid portions of wastewater produced from hydraulic fracturing. These high concentrations often require special treatment in which the solid and liquid portions are separated and then independently treated prior to disposal. The solids are typically disposed in landfills while the liquids are further treated, recycled for future hydraulic fracturing, or disposed via injection wells. Finding optimal treatment methods of both the solid and the liquid fractions requires a thorough understanding of potential Ra mobility from both the raw suspended solids and mineral precipitates formed during treatment. Using a sequential extraction procedure, we found that, without treatment, more than 50% of Ra-226 in the suspended solids was associated with soluble salts and readily exchangeable fractions. When the liquid portion of the wastewater was treated by mixing with acid mine drainage (AMD), which contained high sulfate concentrations, approximately 80–97% of the total Ra-226 in the mixture solution is found in the insoluble sulfate fraction of the precipitate. The activity of Ra-226 sequestered in the precipitated solid sulfate fractions is positively correlated with the Sr/Ba ratio of the wastewater-AMD solution. We discuss implications of these findings for effective long-term management of elevated radium in both solid and liquid wastes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The environmental geochemistry and biology of hydraulic fracturing


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...