Assessing the energy offset at the electron donor/acceptor interface in organic solar cells through radiative efficiency measurements†
Abstract
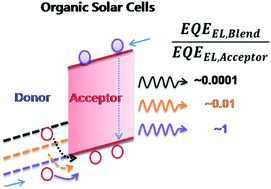
Energy offsets at the electron donor/acceptor interface play an important role in the operation of organic solar cells (OSCs), because their magnitude strongly affects the efficiency of photo-induced charge separation and hence the short-circuit current of a device under illumination. However, quantitative assessment of energy offsets in operating devices remains an open challenge that is still out of the reach of present techniques. Here we show that the ratio of the radiative efficiency (EQEEL) for a blend device to that for the lower bandgap component device (usually a non-fullerene acceptor), namely the EQEEL ratio, can be a strong indicator of the energy offsets in the blend device. In photovoltaic devices based on donors and acceptors with similar backbone structure but varied energy levels, lowering the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) offset increases the open-circuit voltage (VOC) from 0.95 V to 1.05 V, which is consistent with the EQEEL variation trends in the devices. The blend EQEEL approaches that of the emissive low bandgap acceptor when the HOMO of the donor is sufficiently deepened, which at the same time corresponds to a reduction in VOC loss and inefficient photoinduced charge separation. The results suggest that the intrinsic energy loss associated with charge separation can be minimized in practice by minimizing the energy offsets but at the expense of lowering the charge separation efficiency. Statistics from several state-of-the-art material systems reveal that efficient charge generation occurs when the EQEEL ratio is less than 0.1, corresponding to an additional non-radiative voltage loss due to the energy offset of 60 mV. Based on this finding and a modified Shockley–Queisser theory, we estimate an upper thermodynamic efficiency limit for single-junction organic solar cells of about 31%, which is slightly below the Shockley–Queisser limit.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...