Synthesis, characterisation and influence of lipophilicity on cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of unconventional platinum(iv) prodrugs as potent anticancer agents†
Abstract
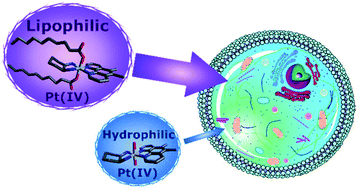
Lipophilic platinum(IV) complexes were synthesised of the type [Pt(HL)(AL)(OH)(R)]2+ and [Pt(HL)(AL)(R)2]2+ (HL = 5,6-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline or 1,10-phenanthroline; AL = 1S,2S-diaminocyclohexane and R = increasingly lipophilic carboxylate axial ligands (C10–18)) from hydrophilic platinum(II) precursors that exhibit exceptional anticancer activity. The increased overall lipophilicity of the complexes suggested the formation of spontaneously self-assembled structures in an aqueous environment. The anti-proliferative properties were assessed against one non-cancerous and a panel of cancerous cell lines. Nanomolar levels of activity were observed against several cell lines, with the lowest GI50 of 3.4 nm against the Du145 prostate cancer cell line and over 1100-fold greater activity than cisplatin against HT29 colon carcinoma. RP-HPLC was utilised to establish the relative lipophilicities of each complex. While there seemed to be an increase in cellular accumulation for the lipophilic derivatives in some instances, ICP-MS studies showed no clear correlation between increasing lipophilicity, cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...