A rhodamine based biocompatible chemosensor for Al3+, Cr3+ and Fe3+ ions: extraordinary fluorescence enhancement and a precursor for future chemosensors†
Abstract
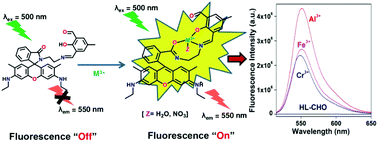
A rhodamine based chemosensor, 3-(((2-(3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2′,7′-dimethyl-3-oxospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-2-yl)ethyl)imino)methyl)-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzaldehyde (HL-CHO), has been developed for the detection of Al3+, Cr3+ and Fe3+ ions. The absorbance of HL-CHO at 528 nm increases significantly in HEPES buffer in methanol : water (9 : 1, v/v) (pH 7.4) in the presence of Al3+, Cr3+ and Fe3+ ions with the alteration of solution color from colorless to pink. The fluorescence intensity of the probe at 550 nm enhances by 1465, 588 and 800 fold in the presence of Al3+, Cr3+ and Fe3+ ions, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this huge increase in fluorescence intensity with Al3+ and Cr3+ has not been observed for other rhodamine based chemosensing systems. The weak fluorescence and no coloration of the probe are due to the existence of a spirolactam ring. The trivalent cations induce the opening of the spirolactam ring and consequently change the color and the fluorescence intensity followed by the 1 : 1 complex formation with HL-CHO which are evident from Job's analysis, ESI mass spectral analysis and elemental analysis. The quantum yield and lifetime of HL-CHO have increased considerably in the presence of the trivalent cations. The high sensitivity of the probe towards all the cations is evident from the nM order of LOD values. This has been used in living cell imaging studies with the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Having appended –CHO groups for Schiff-base condensation with other amines, HL-CHO could be a potential precursor for future chemosensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...