Synthesis, X-ray structure, photophysical properties, and theoretical studies of six-membered cyclometalated iridium(iii) complexes: revisiting Ir(pnbi)2(acac)†
Abstract
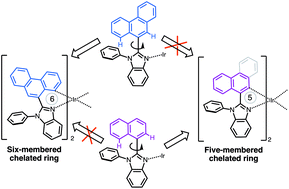
We have determined the X-ray structure of Ir(pnbi)2(acac) (pnbi = 2-phenanthren-9-yl-1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazole; acac = acetylacetonate), which exhibits a six-membered metallocycle around the Ir center. This result stands in sharp contrast to previously postulated structures of Ir(pnbi)2(acac), which assumed a five-membered metallocycle. In this paper, we focus on the relative stability of five- and six-membered Ir(C^N) ring structures. DFT calculations of the total energies of Ir-(C^N) complexes indicated that six-membered structures are more stable when bulky substituents are present in the benzimidazole unit. When the phenanthrene group of pnbi was replaced with a naphthalene moiety, DFT calculations predicted that five-membered cycles are more stable than six-membered rings, which was confirmed experimentally by a single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The steric bulk of the phenanthrene-containing polyaromatic ring ligand thus induces greater interligand repulsion between the two ligands, which plays an important role in determining the cyclometalation route. The Ir complexes examined in this study exhibit red emission (λem ≈ 660 nm) with relatively low quantum yields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...