Geometric considerations of the monoclinic–rutile structural transition in VO2
Abstract
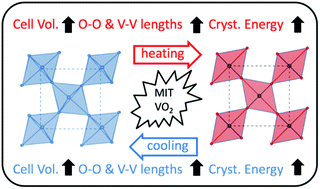
The mechanism of the displacive phase transition in VO2 near the transition temperature is discussed in terms of a geometrical approach, combining simple calculations based on the Brown's band valence model and in situ X-ray diffraction experimental results. Considering that the structural origin is well linked to the electrostatic potential optimization as in a Peierls model, our geometrical calculations and experimental studies are in agreement and suggest that VO2 phase transition is the consequence of very short atomic shifts mainly associated to a decrease of the 2nd sphere coulombic interactions. Hence, at a given temperature, the allotropic form (monoclinic versus rutile form) offering the largest unit-cell volume is stabilized over the lower unit-cell volume allotropic, while the transition occurs at the intercept of the unit cell variation versus temperature of the two forms, which exhibit significantly different thermal expansion coefficients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...