Establishing the correlation between catalytic performance and N→Sb donor–acceptor interaction: systematic assessment of azastibocine halide derivatives as water tolerant Lewis acids†
Abstract
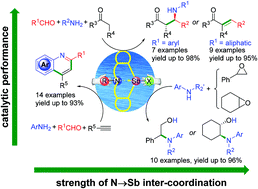
A series of organoantimony(III) halide complexes with a tetrahydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]azastibocine framework were synthesized and employed as water tolerant Lewis acid catalysts. The results of a systematic structure–activity relationship study demonstrated that the strength of N→Sb donor–acceptor interaction could be synergistically modulated by tuning the properties of the nitrogen substituents and halogen atoms adjacent to the central antimony atom, and consequently resulted in distinct catalytic performances towards organic reactions such as Mannich, cross-condensation, cyclization–aromatization and epoxide aminolysis reaction. The fluorinated organoantimony(III) derivatives were found to be more active than those of the chlorinated, brominated and iodinated analogues, owing to the use of an Sb–F moiety as a hydrogen bond acceptor. By comparison, the compound 6-cyclohexyl-12-fluoro-5,6,7,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5] azastibocine (1d) is found to exhibit the highest catalytic activity, together with facile reusability in scale enlarged synthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...