Electronic versus steric control in palladium complexes of carboranyl phosphine-iminophosphorane ligands†
Abstract
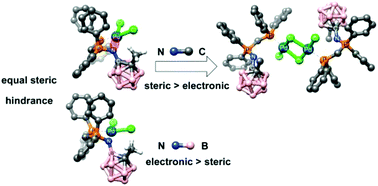
A new family of carboranyl phosphine-iminophosphorane ligands was prepared and characterized. The new ligands present a carboranyl group directly attached to the iminophosphorane nitrogen atom through a cage carbon atom (C-carboranyl derivatives L1–L3) or through the B3 boron atom (B-carboranyl derivatives L4 and L5), and the phosphine group on a side chain derived from the diphosphine dppm, i.e. with a two-atom spacer between the P and N donor atoms. The non-carboranyl analogue L6, with a biphenyl group on the nitrogen atom, was also synthesized for comparison. These potential (P, N) ligands were used to obtain palladium complexes (Pd1–Pd6) and, thus, study how the different inductive effect of the carboranyl substituents can modify the coordinating ability of the nitrogen atom. The structural analysis of the complexes revealed two different coordination modes for the ligands: the (P, N) chelate coordination and the unexpected P-terminal coordination, which is not observed for non-carboranyl phosphine-iminophosphoranes. These unexpected structural differences led us to perform DFT calculations on the ligands and metal complexes. The calculations show that the final coordination modes depend on the balance between the electronic and steric properties of the particular carboranyl group.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...