Silicon-doped graphene edges: an efficient metal-free catalyst for the reduction of CO2 into methanol and ethanol†
Abstract
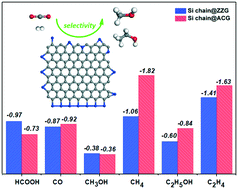
Inspired by a recent study (Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2, 46–54) in which silicon nanosheets decorated with palladium clusters have shown an excellent CO2 reduction activity with the Si atom acting as the catalytic active site, we for the first time identify a metal-free Si-based material for the CO2 reduction reaction (CRR). In experiments, Si atom doped graphene edges (Si@G) have already been realised, and during the preparation of Si@G, Si chain doped graphene edges (Si chain@G) have also been observed with a high percentage (ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 142–149). Due to the “acceptance and back-donation” of electrons between the Si dopant and CO2 molecule, CO2 can be well captured and activated on Si, and in the subsequent reduction process, the formation of CH3OH at the single Si doped armchair edge has the highest activity with a limiting potential of −0.49 V. Since multiple Si active sites are located at the Si chain doped graphene edge, the formation of C2 products, including CH3CH2OH and C2H4, has great probability. DFT calculations have shown that at Si chain@G, the formation of C2H5OH is energetically favourable as compared to C2H4, with a limiting potential of only −0.60 V, which is lower than those of other reported Cu-based materials (such as −1.0 V on the Cu (100) surface). However, the generation of CO and HCOOH has a lower selectivity because of the strong binding strength with the Si atom, making the product desorption difficult. Because of the strong interaction, low limiting potentials and high selectivity, Si@G can be a promising metal-free catalyst to achieve the reduction of CO2, which paves a new way for advancing CO2 conversion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...