Enhancement mechanism of Sn on the catalytic performance of Cu/KIT-6 during the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene†
Abstract
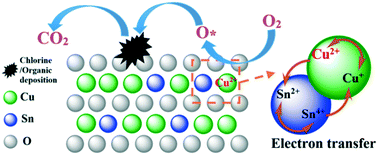
The catalyst SnCu/KIT-6 was prepared via an incipient-wetness impregnation method, and the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene (CB) was investigated. The activation energy (Ea), long-term stabilities, valence state change, solid solution formation, and surficial accumulation compounds (especially for the chlorinated intermediate species) were examined using various analytical techniques, including XRD, N2 adsorption–desorption, TEM, XPS, H2-TPR, TPSR-MS and in situ FTIR. The results showed that the addition of Sn significantly promoted the chlorine resistance and CB oxidation performance of the catalyst. When the Sn/(Cu + Si) molar ratio was equal to 0.1, the SnCu/KIT-6 exhibited the highest reaction rate (r) calculated based on the moles of CB transformed per minute and per square meter from CB conversion (r = 13.2 × 10−3 μmol m−2 min−1). This catalyst also showed excellent stability at 300 °C, and 90% CB conversion can be kept for 80 h. The observations also revealed that the addition of Sn promoted the dispersion of CuO on the support (the major active component in CB oxidation), rearranged the valence distribution (as a result of Sn4+ and Cu+ reaction), increased the surface Cu2+ concentration, and decreased the apparent activation energy (Ea) in CB oxidation. Sn also enhanced the reducibility of the catalyst by forming a SnO2–CuO solid solution and reduced the deposition of chlorine species on the catalyst surface by inhibiting the formation of CuOxCly and enhancing the removal of the chlorine species (in the form of HCl or Cl2). This contributed to the enhanced catalytic performance of SnCu/KIT-6 toward CB oxidation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...