Additive-free cobalt-catalysed hydrogenation of carbonates to methanol and alcohols†
Abstract
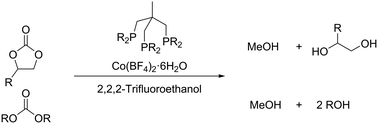
Reduction of various organic carbonates to methanol and alcohols can be achieved in the presence of a molecularly-defined homogeneous cobalt catalyst. Specifically, the use of Co(BF4)2 in combination with either commercial or tailor-made tridentate phosphine ligands allows for additive-free hydrogenations of carbonates. Optimal results are obtained at relatively mild conditions (120 °C, 50 bar hydrogen pressure) in the presence of xylyl-Triphos L4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...