Hydride-catalyzed selectively reductive cleavage of unactivated tertiary amides using hydrosilane†
Abstract
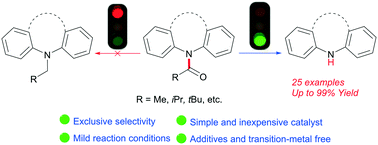
The first hydride-catalyzed reductive cleavage of various unactivated tertiary amides, including the biologically active aryl-phenazine carboxamides and the challenging non-heterocyclic carbonyl functions, using low-cost hydrosilane as a reducing reagent has been developed. The novel catalyst system exhibits high efficiency and exclusive selectivity, providing the desired amines in useful to excellent yields under mild conditions. Overall, this transition metal-free process may offer a versatile alternative to currently employed expensive reducing reagents, high-pressure hydrogen or metal systems for the selective reductive cleavage of amides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...