Rate enhancement by Cu in NixCu1−x/ZrO2 bimetallic catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation of stearic acid†
Abstract
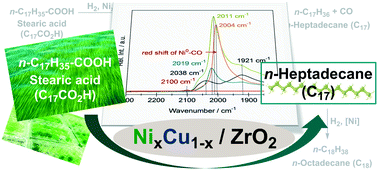
Hydrodeoxygenation of stearic acid on Ni/ZrO2 to n-heptadecane occurs via the reduction to 1-octadecanal, followed by decarbonylation of the aldehyde to n-heptadecane. Stearic acid binds stronger than 1-octadecanal on Ni, causing decarbonylation to start only once stearic acid is almost fully converted. This first step is enhanced by addition of Cu either in the form of Cu/ZrO2 or in the form of a ZrO2 supported NixCu1−x nano-alloy. Cu has not only a higher activity for the reduction of stearic acid, it also increases the activity of Ni for decarbonylation of 1-octadecanal by increasing the electron density of Ni in the bimetal catalyst. The combination of these two effects leads to high activity of Ni–Cu bimetallic catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...