Fe(CN)5@PIL-derived N-doped porous carbon with FeCxNy active sites as a robust electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
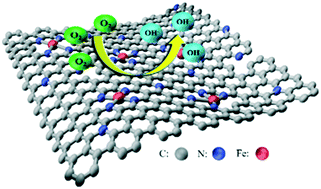
The synthesis and catalytic mechanism of new-type Fe–N co-doping catalysts are important topics for the research on fuel cells. Herein, we report the synthesis and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) properties of a new Fe–N co-doping carbon composite using poly(ionic liquid)s and ferric salt as precursors. The structural characterizations revealed that the as-prepared material features ordered porous properties with a specific surface area of 719.1 m2 g−1, corresponding to FeCxNy/N-doped porous carbons (FeCxNy/N-PC). The electrochemical measurements indicated they show superior catalytic activity (Tafel slope of 70.8 mV dec−1 and E1/2 of 0.84 V), stability and high methanol tolerance compared to the commercial Pt/C catalyst. Furthermore, density functional theory calculations uncovered that the FeCxNy/N-PC composite catalyzes the ORR according to the four-electron associative mechanism with the free-energy barrier of 0.51 eV in the rate-determining formation of H2O. Interestingly, the electronic structure analysis demonstrated the FeCxNy particles serve as active sites and the synergistic effect of the Fe and N atoms of N-PC can promote the ORR performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...