Thermoelectric power factor of pure and doped ZnSb via DFT based defect calculations†
Abstract
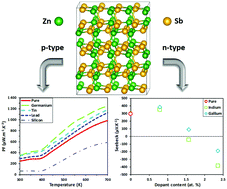
The power factor of pure p-type ZnSb has been calculated via ab initio simulations assuming that the carrier concentrations are due to the doping effect of intrinsic zinc vacancies. With a vacancy concentration close to the experimental solubility limit we were able to perfectly reproduce the Power Factor measured in polycrystalline ZnSb samples. The methodology has then been successfully extended for predicting the effect of extrinsic doping elements on the thermoelectric properties of ZnSb. Germanium and tin seem to be promising p-type doping elements. In addition, we give, for the first time, an explanation of why it is difficult to synthesize polycrystalline n-type ZnSb samples. Indeed, compensative effects between intrinsic defects (zinc vacancies) and doping elements (Ga, or In) explain the existence of an optimal (and relatively high) dopant concentration necessary to convert ZnSb into an n-type semiconductor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...