The effect of dimerization on the activation and conformational dynamics of adenosine A1 receptor†
Abstract
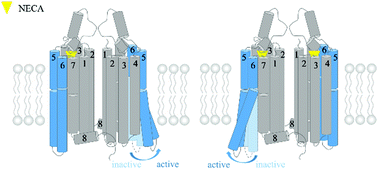
The adenosine A1 receptor (A1R) is one of four adenosine receptors in humans, which are involved in the function of the cardiovascular, respiratory and central nervous systems. Experimental results indicate that A1R can form a homodimer and that the protomer–protomer interaction in the A1R dimer is related to certain pharmacological characteristics of A1R activation. In this work, we performed docking, metadynamics simulation, conventional molecular dynamics simulations, Gaussian-accelerated molecular dynamics simulations, potential of mean force calculations, dynamic cross-correlation motions analysis and community network analysis to study the binding mode of 5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) to A1R and the effect of dimerization on the activation of A1R. Our results show that NECA binds to A1R in a similar mode to adenosine in the A1R crystal structure and NECA in the A2AR crystal structure. The A1R homodimer can be activated by one or two agonists with NECA occupying its orthosteric pockets in one (which we call the NECA–A1R system) or both protomers (which we call the dNECA–A1R system). In the NECA–A1R system, activation is predicated in the protomer without NECA bound. In the dNECA–A1R system, only one protomer achieves the active state. These findings suggest an asymmetrical activation mechanism of the homodimer and a negative cooperativity between the two protomers. We envision that our results may further facilitate the drug development of A1R.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...