Molecular dynamics involving proton exchange of a protic ionic liquid–water mixture studied by NMR spectroscopy†
Abstract
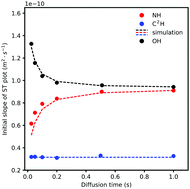
Protic ionic liquids (PILs) are proposed as alternative anhydrous proton conducting electrolytes for intermediate temperature fuel cells. One of the key factors in their performance as electrolytes, as far as charge transport is concerned, is their proton conductivity. Noting the success of water-containing electrolytes and recognising faster proton mobility than structural relaxation (via mechanisms such as Grotthuss) as their advantage, such an advantage is envisaged for PILs and in some cases deduced. As extended hydrogen bond networks and proton exchange are at the heart of these mechanisms, here we report our results on a prototypical characterisation of proton exchange in a PIL (C2HimNTf2)–water mixture. NMR lineshape analysis and exchange spectroscopy (EXSY) are used to quantify the proton exchange rate. The obtained exchange rate is then used to explain the diffusion behaviour of the exchangeable proton as measured by pulse field gradient NMR methods; a marginal anomaly in the translational dynamics of the exchangeable proton in the form of a faster NH proton is observed. As far as we know this is the first report on systematic characterisation of proton exchange in PILs with the aim of understanding its effect on translational motion as a way of discerning exchange related mobility anomalies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...