Molecular kinetics and cooperative effects in friction and adhesion of fast reversible bonds
Abstract
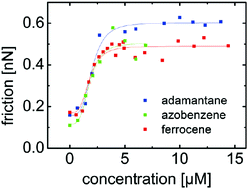
Molecular mechanisms of adhesion and friction include the rupture of single and multiple bonds. The strength of adhesion and friction thus depends on the molecular kinetics and cooperative effects in the lifetime of bonds under stress. We measured the rate dependence of friction and adhesion mediated by supramolecular guest–host bonds using atomic force microscopy (AFM). The tip of the AFM and the surface were functionalized with cyclodextrin hosts. The influence of molecular kinetics on adhesion and friction was studied using three different ditopic guest molecules that connected the AFM tip and the surface. Adamantane, ferrocene, and azobenzene were the guest end groups of the connector molecules that formed inclusion complexes with the cyclodextrin hosts. The results confirm the importance of the molecular off-rate and of cooperative effects for the strength of adhesion and friction. Positive cooperativity also shapes the dependence of friction on the concentration of connector molecules, which follows the Hill–Langmuir model. Based on the Hill coefficient of 3.6, reflecting a characteristic rupture of at least 3–4 parallel bonds, a rescaling of the pulling rate is suggested that shifts the rate dependence of adhesion and friction for the three different molecules towards one master curve.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...