On the ubiquity of helical α-synuclein tetramers†
Abstract
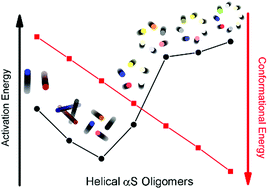
The experimental finding that α-synuclein (αS) occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer begs the question: why are helical tetramers the most populated multimers? While the helical tetramer is known to resist aggregation, the assembly mechanism of αS peptides remains largely unknown. By rationally designing a series of helical multimers from dimer to octamer, we characterized the free energy landscape of wild-type and mutated multimers using molecular dynamics computer simulations. Competition between supramolecular packing and solvation results in well-hydrated dimers and trimers, and more screened pentamers to octamers, with the helical tetramer possessing the most balanced structure with the lowest activation energy. Our data suggest that familial mutants are very sensitive to alterations in monomer packing that would in turn raise the energy barriers for multimerization. Finally, the hypothesis that the αS tetramer forms a soluble, benign “dead end” to circumvent aggregation is supported by its computed very weak association with negatively charged cell membranes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...