Co-incorporation of alkali metal ions during amorphous calcium carbonate precipitation and their stabilizing effect†
Abstract
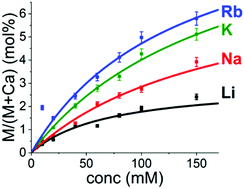
Calcium carbonate formation has been studied extensively due to its central role in biomineralization and geochemistry. Specifically, the effect of additives incorporated during the formation process has been described in several works related to inorganic, small organic, molecular or macromolecular additives. However, in these previous experiments the presence of counter ions and their possible role has been mostly disregarded. Co-incorporation of counter ions into calcite at low supersaturations has been studied in detail but their incorporation in and effect on the formation and stability of the amorphous phase, which precedes the formation of the crystalline phase at high supersaturations, has not been studied. To address this, we have investigated the incorporation of alkali metal ions into the amorphous phase using various carbonate salts as a carbonate source. We show that the incorporation is the highest for Rb+ with the highest measured value being 5.8 at% Rb+/(Rb+ + Ca2+). The extent of ion incorporation follows the ion size of Rb+ > K+ > Na+ > Li+ which is opposite to that observed in calcite formed at low supersaturation. The presence of these ions in the amorphous phase increases the crystallization temperature, which can be shifted by as much as 200 °C depending on the concentration of alkali metal ions incorporated. However, the lifetime of ACC in solution was similar for all the different carbonate sources.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...