Chain length effect on thermal transport in amorphous polymers and a structure–thermal conductivity relation†
Abstract
The physics of thermal transport in polymers is important in many applications, such as in heat exchangers and electronics packaging. Even though thermal conductivity models for amorphous polymers have been reported since the 1970s, none of the published models included the chain conformation and chain stiffness effects. In this study, we use molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to study the chain length effect on thermal conductivity of amorphous polyethylene (PE), and the number of repeating C2H4 units ranges from 5 to 200. The total thermal conductivity is decomposed into its contributions from energy convection (k-convection), and heat transfer through nonbonding (k-nonbonding) and bonding (k-bonding) interactions. Each part of the contributions is fitted empirically by using a scaling relationship: k-convection 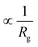 (Einstein's diffusion coefficient model), k-nonbonding ∝ n (Choy's model) and k-bonding
(Einstein's diffusion coefficient model), k-nonbonding ∝ n (Choy's model) and k-bonding 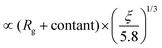 (from this study), where Rg is the radius of gyration, n is the number density, and ξ is the persistence length. Summarizing these three components, we emphasize the chain conformation (Rg) and chain stiffness (ξ) effects on thermal conductivity, and we propose a structure–property relation model for amorphous polymers. Our empirical model is compared with Hansen's experimental data [D. Hansen, R. Kantayya and C. Ho, Polym. Eng. Sci., 1966, 6, 260–262] and with our MD results. Our empirical model relies on realistic structural properties to enable accurate predictions. We believe that our model has captured some key structure–property relations in amorphous polymers.
(from this study), where Rg is the radius of gyration, n is the number density, and ξ is the persistence length. Summarizing these three components, we emphasize the chain conformation (Rg) and chain stiffness (ξ) effects on thermal conductivity, and we propose a structure–property relation model for amorphous polymers. Our empirical model is compared with Hansen's experimental data [D. Hansen, R. Kantayya and C. Ho, Polym. Eng. Sci., 1966, 6, 260–262] and with our MD results. Our empirical model relies on realistic structural properties to enable accurate predictions. We believe that our model has captured some key structure–property relations in amorphous polymers.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...