Ammonolysis as an important loss process of acetaldehyde in the troposphere: energetics and kinetics of water and formic acid catalyzed reactions†
Abstract
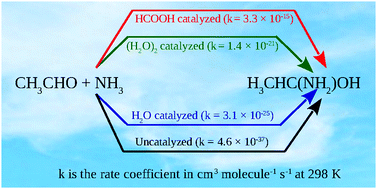
The reaction of ammonia with acetaldehyde as a potential source of 1,1-aminoethanol in the troposphere has been investigated by electronic structure and chemical kinetics calculations. The reaction was found to involve very high activation energy and consequently the rate coefficient value was found to be too small to have any significant atmospheric implication. Therefore, the catalytic effects of water (monomer and dimer) and formic acid on the reaction have also been studied. The water catalyzed reaction involves significantly lower barrier height, more so for dimer than monomer, whereas formic acid makes the reaction effectively barrierless. In terms of rate coefficients too, formic acid was found to be the most efficient followed by water dimer and monomer. Further, comparative studies under various tropospheric conditions among the catalyzed reaction channels have been carried out using relative rate calculations with respect to the uncatalyzed channel. Relative rate calculations indicate that the formic acid catalyzed channel would dominate over the water catalyzed channels at 0 km altitude when the concentration of the former is high, but water catalyzed channels would dominate under hot and humid conditions if the concentration of formic acid remains low. At higher altitudes in the troposphere, 1,1-aminoethanol formation through ammonolysis of acetaldehyde would almost exclusively follow the formic acid catalyzed channel.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...