Neutron reflectometry to measure in situ the rate determining step of lithium ion transport through thin silicon layers and interfaces†
Abstract
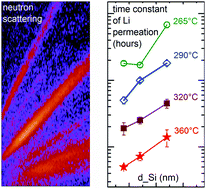
Li ion transport through thin (14–22 nm) amorphous silicon layers adjacent to lithium metal oxide layers (lithium niobate) was studied by in situ neutron reflectometry experiments and the control mechanism was determined. It was found that the interface between amorphous silicon and the oxide material does not hinder Li transport. It is restricted by Li diffusion in the silicon material. This finding based on in situ experiments confirms results obtained ex situ and destructively by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) depth profiling investigations. The Li permeabilities obtained from the present experiments are in agreement with those obtained from ex situ SIMS measurements showing similar activation enthalpies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...