Radiolysis of supercritical water at 400 °C: density dependence of the rate constant for the reaction of hydronium ions with hydrated electrons
Abstract
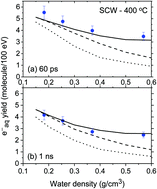
The rate constant, k(eaq− + H3O+), for the reaction of hydronium ions with hydrated electrons in supercritical water (SCW) at 400 °C has been evaluated as a function of water density using Monte Carlo track chemistry simulations of the radiolysis of SCW over the range of 0.15–0.6 g cm−3. Results are consistent with recent predictions using the so-called “cage effect” model.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...