Unambiguous hydrogenation of CO2 by coinage-metal hydride anions: an intuitive idea based on in silico experiments†
Abstract
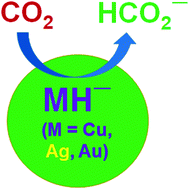
Gas phase hydrogenation of CO2 to HCO2− by coinage-metal hydride anions, MH− (M = Cu, Ag and Au), has been studied with the help of high level computational methodologies. We demonstrate that these hydride anions perform excellently in the specific hydrogenation of CO2 to HCO2−. More precisely, AgH− is shown to be very active for this particular purpose. We show that CO2 activation through the M–H⋯CO2 pathway passes through a very low energy barrier and produces HCO2−; even the metal centered activation (H–M⋯CO2) also leads to the same product through an energy barrier less than 15 kcal mol−1. A closer inspection demonstrates that electronegativity, size of the metal and hydricity of the MH− species control the overall hydrogenation process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...