Theoretical study of C-arylations with aryl halides to determine the reaction mechanism, the effect of substituents and heteroatoms†
Abstract
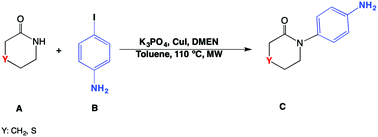
Carbon arylations are very important in the pharmaceutical industry. New synthesis routes are often studied with the objective of trying to insert new bonds and substituents into an organic framework. Ullman reactions have been very useful in this context. In light of this, a wB97XD/6-311g set of Ullman-like reactions among substituted amide arylations with iodoaniline were theoretically studied in order to understand their intrinsic reactivity and their reaction mechanisms. The studied systems included unsubstituted (C), sulphur (S), synthesized by the authors in a previous experimental work. In this study, amino (NH) and butyloxycarbonyl (NBoc) amides were added. IRC calculations on catalyzed species showed that the catalyst lowers the reaction barrier, and changes the reactivity in order to lower the nitrogen charge. The reaction mechanism proceeds by binding the CuI catalyst and N,N-dimethylethylenediamine (DMEN) to the N lactam, in a barrierless reaction, thereby activating the nitrogen to bond with the aryl iodine through a nucleophilic substitution, and thus recovering the catalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...