Reaction pathways for HCN on transition metal surfaces†
Abstract
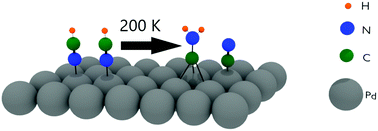
The adsorption and decomposition of HCN on the Pd(111) and Ru(001) surfaces have been studied with reflection absorption infrared spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations. The results are compared to earlier studies of HCN adsorption on the Pt(111) and Cu(100) surfaces. In all cases the initial adsorption at low temperatures gives rise to a ν(C–H) stretch peak at ∼3300 cm−1, which is very close to the gas phase value indicating that the triple CN bond is retained for the adsorbed molecule. When the Pd(111) surface is heated to room temperature, the HCN is converted to the aminocarbyne species, CNH2, which was also observed on the Pt(111) surface. DFT calculations confirm the high stability of CNH2 on Pd(111), and suggest a bi-molecular mechanism for its formation. When HCN on Cu(100) is heated, it desorbs without reaction. In contrast, no stable intermediates are detected on Ru(001) as the surface is heated, indicating that HCN decomposes completely to atomic species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...