Mutual energy transfer luminescent properties in novel CsGd(MoO4)2:Yb3+,Er3+/Ho3+ phosphors for solid-state lighting and solar cells†
Abstract
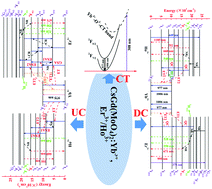
In this work, we prepared a novel kind of Yb3+,Er3+/Ho3+ co-doped CsGd(MoO4)2 phosphors with a different structure from the reported ALn(MoO4)2 (A = Li, Na or K; Ln = La, Gd or Y) compounds using a high-temperature solid-state reaction method. X-ray diffraction showed that the as-prepared samples had a pure phase. Based on the efficient energy transfer from Yb3+ to Er3+/Ho3+, the up-conversion (UC) luminescence of the optimal CsGd(MoO4)2:0.30Yb3+,0.02Er3+ sample showed intensely green light with dominant emission peaks at 528 and 550 nm corresponding to Er3+ transitions 2H11/2 → 4I15/2 and 4S3/2 → 4I15/2, respectively, as well as a weak emission peak originating from 4F9/2 → 4I15/2 at 671 nm, under 975 nm laser excitation. The CsGd(MoO4)2:Yb3+,Ho3+ samples mainly displayed two emission bands around 540 and 660 nm together with a negligible one at 755 nm, which corresponded to Ho3+ transitions 4F4,5F2 → 5I8, 5F5 → 5I8 and 4F4,5F2 → 5I7, respectively, under 975 nm laser excitation. With increasing Yb3+ concentration in CsGd(MoO4)2:Yb3+,Ho3+ phosphors, the emission color could be tuned from orange red to light yellow due to the large energy gap between levels 4F4,5F2 and 5F5. In addition, the CsGd(MoO4)2:Yb3+,Er3+ showed green light under 376 nm UV irradiation similar to that upon 975 nm laser excitation. However, the emissions for CsGd(MoO4)2:Yb3+,Ho3+ samples under 358 nm UV or 449 nm blue excitation showed dominant emission peaks at 540 nm and weak 660 nm and 752 nm peaks, which were a bit different from those under 975 nm excitation. Interestingly, we observed efficient energy transfer phenomena (possible quantum cutting) from Er3+/Ho3+ to Yb3+ and a Yb3+–O2− charge transfer (CT) transition in the molybdates, which was deduced from the visible and near-infrared emission spectra and the decrease of the Er3+/Ho3+ luminescent lifetimes with increasing Yb3+ concentration in the CsGd(MoO4)2:Yb3+,Er3+/Ho3+ samples. The luminescence properties of these phosphors suggest their potential possibility for applications in solid-state lighting and displays as well as in c-Si solar energy conversion systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...