The basis for reevaluating the reactivity of pyrite surfaces: spin states and crystal field d-orbital splitting energies of bulk, terrace, edge, and corner Fe(ii) ions†
Abstract
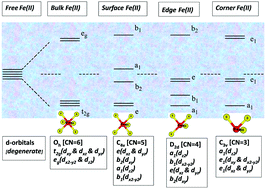
Pyrite, one of the most important minerals to catalyze redox reactions in nature and a bulk low-spin Fe mineral, needs to provide high-spin Fe on surfaces to moderate spin-forbidden transitions. Here, the spin state of pyrite is investigated using density functional theory (DFT) calculations on cluster and periodic models. The energies of clusters FexS2x (where x = 4, 8, 16, and 32) were calculated as a function of total spin and different up/down spin configurations. The undercoordinated Fe on surfaces, edges, and corners were found to provide intermediate and high-spin Fe necessary for catalysis. Generally, the lower the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE), Δ, for a particular Fe atom, the higher is the spin density. Pyrite bulk (3D) and surfaces (2D) (+ water to mimic aqueous systems) were examined. The calculated bulk band gap (0.95 eV) is in excellent agreement with previous reports. For the surface, a conducting state is predicted. The calculated CFSE for bulk Fe(II) in pyrite (∼2.2 eV) agrees with previous CFT results; due to surface states, this CFSE decreases to ∼1 eV on terraces. This study highlights the importance of accurately describing the spin state of pyrite.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...