Covalently assembled dopamine nanoparticle as an intrinsic photosensitizer and pH-responsive nanocarrier for potential application in anticancer therapy†
Abstract
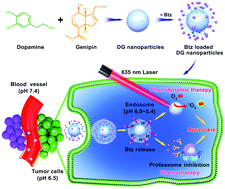
We report a novel nanophotosensitizer via one-step covalent assembly of dopamine and genipin. This is the first report unveiling the photodynamic effect of dopamine-based materials. These nanophotosensitizers can also act as pH-responsive drug nanocarriers via a catechol–boronate linkage, thus achieving combined PDT and chemotherapy for highly efficient cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...