An amphipathic cell penetrating peptide aids cell penetration of cyclosporin A and increases its therapeutic effect in an in vivo mouse model for dry eye disease†
Abstract
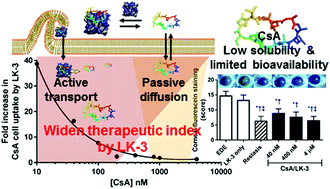
Cell penetrating peptide (CPP), LK-3, causes a ca. 10-fold increase in the cell penetration of cyclosporin A (CsA) at nanomolar concentrations. The results of an in vivo dry eye mouse model demonstrated that a 100-fold lower dose of the CsA/LK-3 complex than that of Restasis® is sufficient to cause the same therapeutic effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...