Bi-inorganic-ligand coordinated colloidal quantum dot ink†
Abstract
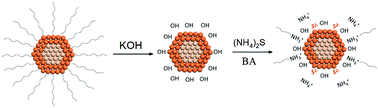
Quantum dot light emitting diodes (QLEDs) are rising as a promising light emitting technology. However, the widely used insulating organic ligands hamper carrier injection. Herein, we developed a bi-inorganic-ligand strategy to replace organic ligands and dispersed QDs in a benign solvent butylamine. The all-inorganic QD film shows enhanced luminescence intensity and superior thermal stability and conductivity. In the end, we exploited the first prototype all inorganic QLED.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...