New insights into the metal-induced oxidative degradation pathways of transthyretin†
Abstract
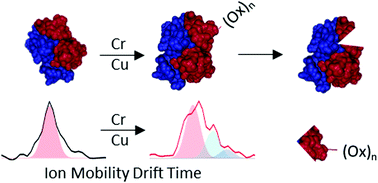
The amyloidogenic mechanism of transthyretin is still debated but understanding it fully could lend insight into disease progression and potential therapeutics. Transthyretin was investigated revealing a metal-induced (Cr/Cu) oxidation pathway leading to N-terminal backbone fragmentation and oligomer formation; previously hidden details were revealed only by FT-IM-Orbitrap MS and surface-induced dissociation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...