Efficient discovery of novel antimicrobials through integration of synthesis and testing in crude ribosome extract†
Abstract
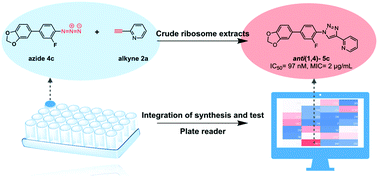
By coupling in situ [2+3] Huisgen cycloaddition with an in vitro transcription/translation luminescence assay in a crude ribosomal extract, a robust and accurate high-throughput platform was successfully developed and applied for efficient identification of novel structural types of ribosomal inhibitors with antimicrobial activity against drug-resistant bacteria.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...