A biofunctionalized viral delivery patch for spatially defined transfection†
Abstract
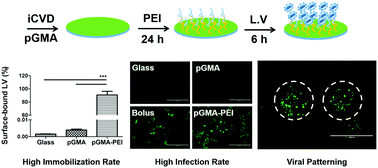
Gene therapy holds the significance of correcting genetic defects. However, difficulties in the in vivo delivery to the targeted tissues and systemic delivery remain the biggest challenges to be overcome. Here, a robust system of biofunctionalized polymeric layer-mediated lentiviral delivery was designed for the site-specific spatial and temporal control of viral gene delivery. Poly glycidyl methacrylate (pGMA) modification of a substrate via initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) followed by polyethyleneimine (PEI) immobilization provided the adhesion site for the lentivirus. Furthermore, the polymeric patch based gene delivery system showed a high rate of gene transduction compared to bolus treatment. Furthermore, by using mask patterning, we were able to spatially pattern the lentivirus which allowed spatially defined transfection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...