Triple bonds between iron and heavier group-14 elements in the AFe(CO)3− complexes (A = Ge, Sn, and Pb)†
Abstract
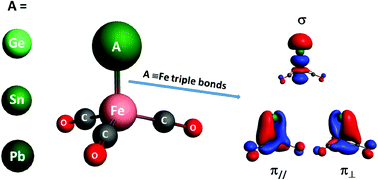
Heteronuclear transition-metal-main-group element carbonyl anion complexes of AFe(CO)3− (A = Ge, Sn, and Pb) are prepared using a laser vaporization supersonic ion source in the gas phase, which were studied by mass-selected infrared (IR) photodissociation spectroscopy. The geometric and electronic structures of the experimentally observed species are identified by a comparison of the measured and calculated IR spectra. These anion complexes have a 2A1 doublet electronic ground state and feature an A![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Fe triply bonded C3v structure with all of the carbonyl ligands bonded at the iron center. Bonding analyses of AFe(CO)3− (A = C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, and Fl) indicate that the complexes are triply bonded between the valence np atomic orbitals of bare group-14 atoms and the hybridized 3d and 4p atomic orbitals of iron.
Fe triply bonded C3v structure with all of the carbonyl ligands bonded at the iron center. Bonding analyses of AFe(CO)3− (A = C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, and Fl) indicate that the complexes are triply bonded between the valence np atomic orbitals of bare group-14 atoms and the hybridized 3d and 4p atomic orbitals of iron.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...