Dynamic split G-quadruplex programmed reversible nanodevice†
Abstract
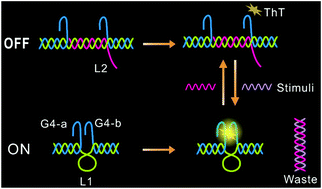
We propose a dynamic nanodevice based on a split G-quadruplex (G4). By splitting it apart, we can successfully decouple the G-tetrad formation from external stimuli, greatly expanding the stimulus for G4 based devices. Taking advantage of the rigid force from a DNA duplex, the nanodevice can be switched reversibly through the conformational transformation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...