Application of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for degradation of the bacterial autoinducer N-hexanoyl homoserine lactone†
Abstract
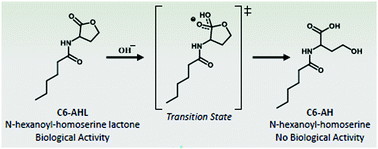
A novel bacterial quorum quenching system is presented. For the first time the degradation of N-L-hexanoyl homoserine lactone (C6-AHL), a Gram-negative quorum sensing autoinducer, has been enhanced using molecularly imprinted nanoparticles (MIP NPs) which were prepared using transition state analogue of the γ-lactone ring hydrolysis as template.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...