Construction, mechanism, and antibacterial resistance insight into polypeptide-based nanoparticles†
Abstract
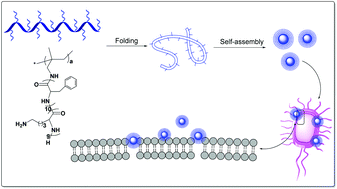
The emergence of drug-resistant bacteria poses a serious threat to public health. The traditional antibiotics have specific intracellular targets and disinfect via chemical ways, which easily lead to the development of drug resistance, therefore, cationic peptides as promising antibiotic agents have attracted extensive attention due to their unique properties. Herein, we report a class of amphiphilic peptide-based pectinate polymers with primary amino groups. The polymers spontaneously self-assembled into the positively charged nanoparticles, which were evaluated and confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Biological assays revealed that the nanoparticles showed broad-spectrum antibacterial efficacy against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, exhibiting a MIC of 16 μg mL−1 against six clinical bacteria, namely, E. faecalis, S. aureus, MRSA, VRE, P. aeruginosa, and K. pneumonia, and three bacterial strains E. coli and E. coli producing NDM-1 and ImiS, and showed a sterilization rate of 95.6% and 94.7% on S. aureus and E. coli, respectively. Importantly, the nanoparticles did not result in drug-resistance for both the normal and drug-resistant bacteria tested after 14 passages and showed low toxicity on the mouse fibroblast cells (L929). The fluorescence staining, electrical conductivity, SEM, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) characterization suggested that the nanoparticles initially bound to the surface of the bacteria, then pierced into the membranes of the bacteria with their phenyl groups, and finally disrupted the membranes, resulting in ions leaking out and thus exhibiting broad-spectrum antibacterial efficacy. This bactericidal mechanism that the nanoparticles employed does not lead the bacteria susceptible to developing drug resistance. This study provides a promising pathway for the development of the efficient antibacterial materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...