Cysteine-based redox-responsive nanoparticles for small-molecule agent delivery†
Abstract
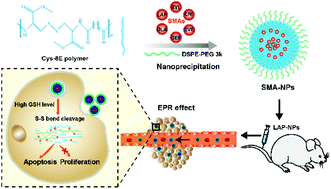
As a significant part of molecular-targeted therapies, small-molecule agents (SMAs) have been increasingly used for cancer treatment. Nevertheless, most SMAs are currently administered orally due to their poor solubility, resulting in a low bioavailability and unavoidable side effects. Herein, we proposed a promising SMA delivery strategy using a biocompatible and redox-responsive nanoparticle (NP) delivery system to improve their bioavailability, alleviate side effects and enhance therapeutic performance. To demonstrate the feasibility of this strategy, a type of cysteine-based hydrophobic polymer was employed to construct a redox-sensitive nanoplatform for the delivery of various hydrophobic oral SMAs. These SMA-loaded nanoparticles (SMA-NPs) all have a small particle size and good drug-loading capacity. Particularly, lapatinib-loaded nanoparticles (LAP-NPs) with a minimal particle size (79.71 nm) and an optimal drug-loading capacity (12.5%) were utilized as a model to systemically explore the in vitro and in vivo anticancer potential of SMA-NPs. As expected, the LAP-NPs exhibited rapid redox-responsive drug release, enhanced in vitro cytotoxicity and cell apoptosis, and demonstrated notable anti-metastasis ability and desirable intracellular localization. Additionally, the in vivo results demonstrated the preferential accumulation of LAP-NPs in tumor tissues and the significant suppression of tumor growth. Therefore, the generated SMA-NP delivery system shows great SMA delivery potential for advanced molecular-targeted therapies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...