Sulfosalicylic acid/Fe3+ based nanoscale coordination polymers for effective cancer therapy by the Fenton reaction: an inspiration for understanding the role of aspirin in the prevention of cancer†
Abstract
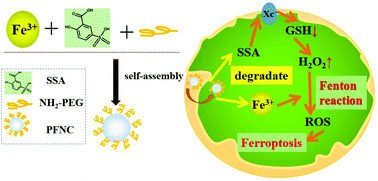
Fenton reaction-based reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation provides a new idea for the design of ROS-mediated anticancer agents. Finding ways to increase iron uptake and to elevate the level of H2O2 in cells simultaneously is thus crucial to this strategy. Meanwhile, salicylic acid (SA) or its analogue, as the major metabolite of aspirin, has been reported to be closely associated with an intracellular redox-active product. In this work, a PEG-modified nanoscale coordination polymer (PFNC) via the self-assembly of 5-sulfosalicylic acid (SSA) with Fe3+ ions has been designed for the first time. The results show that the SSA dissociated from the PFNC can lead to the decrease of GSH and the accumulation of H2O2 in cancer cells, and thus elevate cellular ROS via the Fenton reaction. Owing to such intracellular oxidative stress, PFNC-induced ferroptotic cell death was further confirmed. In vitro cytotoxicity studies show that PFNCs display higher cytotoxicity on cancer cells than on normal cells. In vivo experiments further demonstrate that PFNCs not only possess high tumor accumulation, but also significantly inhibit the tumor growth without obvious damage toward the major organs. Based on the results, we expect that this work will provide an inspiration for understanding the role of SA, even aspirin, in the prevention of cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...