Exploring the potential of high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry towards non-destructive control and validation of electroless gold nanoparticles onto silicon nanowires hybrids†
Abstract
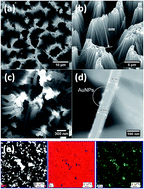
The manufacturing of conventional electroless-based sensors often suffers from mechanical instability leading to irreversible changes in the sensor architecture and morphology resulting in insufficient signal reproducibility and overall degradation of the system. In addition, understanding the transduction mechanisms is a key aspect in the development of crucial sensing technologies. Therefore, the development of tools and analytical approaches that could allow us to gain deeper insight into the operating processes or validation of the design would significantly accelerate the progress in the field of sensors. Herein, we present a novel effective strategy for non-destructive control and validation of sensors consisting of hybrid silicon nanowires deposited with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs/SiNWs) produced via a hydrofluoric acid-assisted electroless fabrication method. To validate the fabrication method and to monitor the deposition rates of hydrofluoric acid-assisted deposition of AuNPs on SiNWs, specific analytical protocols for high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HR-ICP-MS) and electron microscopy (SEM/TEM) were developed. Moreover, HR-ICP-MS was used for the non-destructive monitoring of the impact of experimental conditions on the quality of the synthesized hybrid nanostructures. Thus, the impact of certain synthesis conditions, viz. acid ratio, deposition time and surface pretreatment, on the deposition rates, morphology and stability of the prepared AuNPs/SiNWs hybrid structures was investigated in detail. The obtained knowledge based on nanoanalytical studies was applied to develop hybrids with a reproducible surface morphology, homogenous AuNPs distribution and stable attachment to the SiNWs surface to be implemented as reliable substrates for surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...