A hydrogel sensor-based microfluidic platform for the quantitative and multiplexed detection of fertility markers for point-of-care immunoassays†
Abstract
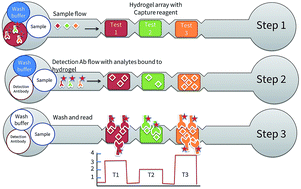
We report a new microfluidics-based immunoassay platform based on 3D porous hydrogel particle sensors with planar rectangular geometries. Large numbers of sensors are made off-chip before being embedded into an injection molded microfluidic chip. This allows for both multiplexing and scalability of manufacturing processes. A specially designed adapter containing detection reagents and buffers is interfaced with a microfluidic chip allowing for an automated immunoassay to be performed. All antibody reagents required for the test are stored in a dried form on the chip, enabling stability for resource-limited settings. Fluorescence-based immunoassays are performed by a sequential flow of the sample, detection reagents and wash buffer over the sensors. A compact instrument that integrates microfluidic flow dispensing and pumping with highly sensitive array-based detection is used to conduct and read the assay. A multiplexed set of 4 important fertility-linked tests, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and prolactin (PRL), that are commonly required at gynecology/IVF settings were developed and validated using discarded clinical samples. Detailed data on accuracy, precision, linearity, effects of interference and cross-reactivity have been studied, rendering the platform ready for clinical use.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...